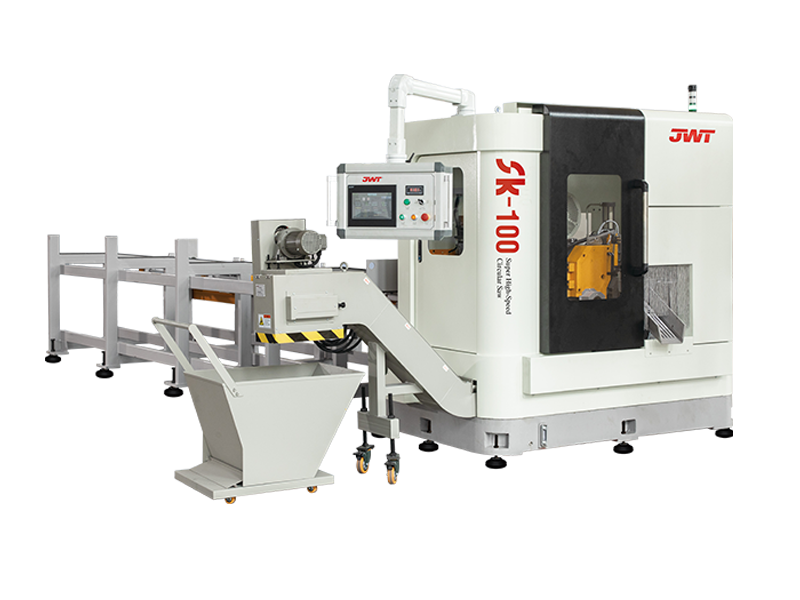
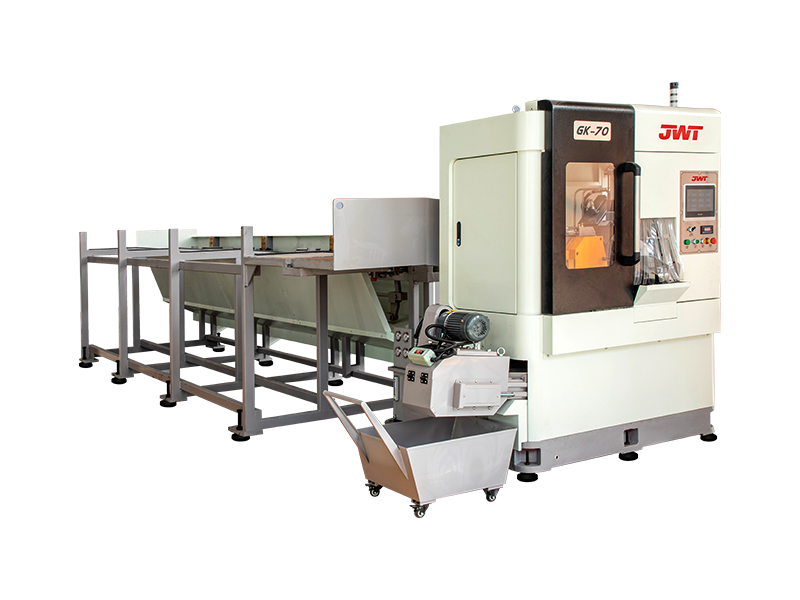
What functions does Automatic Saw Machine have?
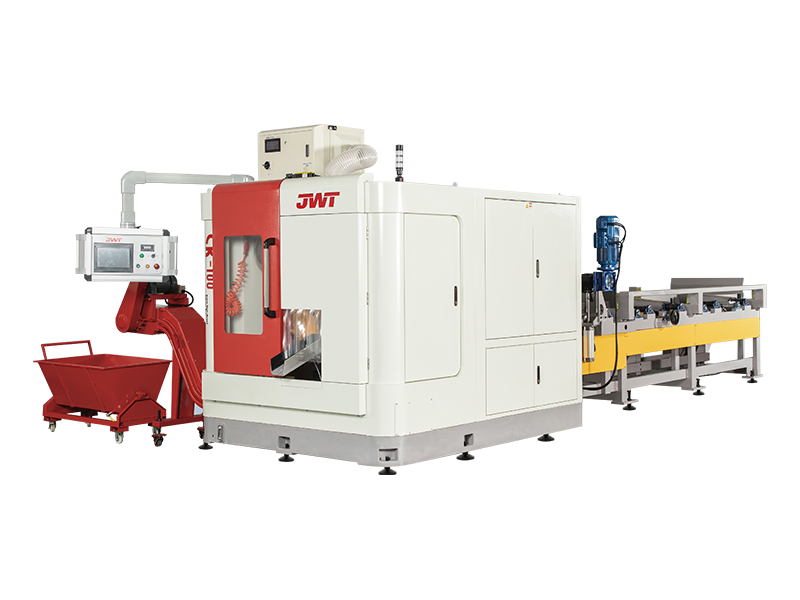
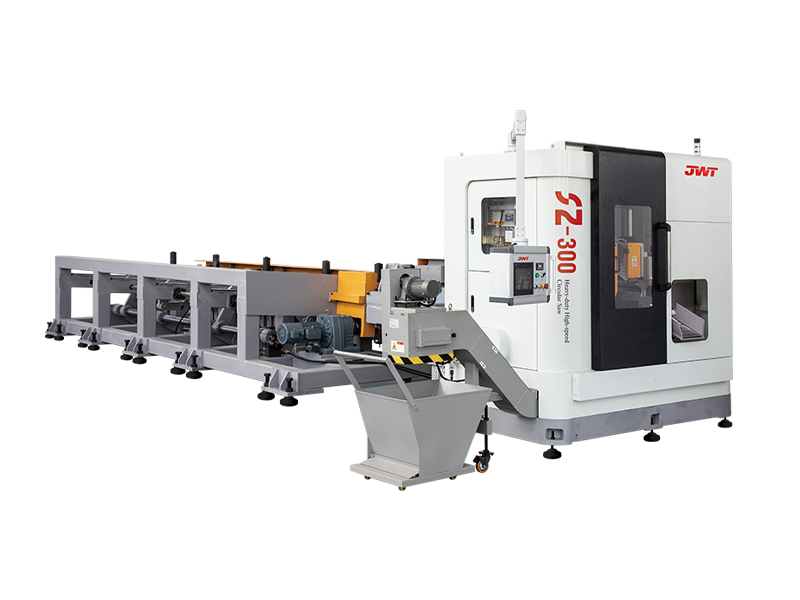
Automatic saw machines, often referred to as automated cutting systems or CNC saws, are indispensable tools in modern manufacturing and fabrication. Their ability to precisely and efficiently process a wide range of materials has revolutionized industries from woodworking and metalworking to construction and plastics. Far beyond simply "sawing," these sophisticated machines offer a suite of functions that optimize production, enhance safety, and improve material utilization.
Precision Cutting and Sizing
At its core, the primary function of an automatic saw machine is precision cutting. Unlike manual operations, these machines leverage advanced controls to achieve highly accurate dimensions and clean cuts, minimizing waste and ensuring product quality. Whether it's cutting lumber for construction, sizing metal profiles for industrial machinery, or segmenting plastic sheets for custom parts, the automated saw consistently delivers:
-
Exact Lengths and Angles: Programmed with specific dimensions, they can cut materials to precise lengths and at various angles (e.g., miter cuts, bevels), often with tolerances of fractions of a millimeter.
-
Repetitive Accuracy: For high-volume production, the machine performs identical cuts repeatedly, ensuring uniformity across all manufactured pieces. This is crucial for assembly processes where consistency is key.
-
Minimized Kerf Loss: Modern automatic saws are designed to optimize blade thickness and cutting paths, reducing the amount of material lost as sawdust or chips (kerf loss).
Material Handling and Optimization
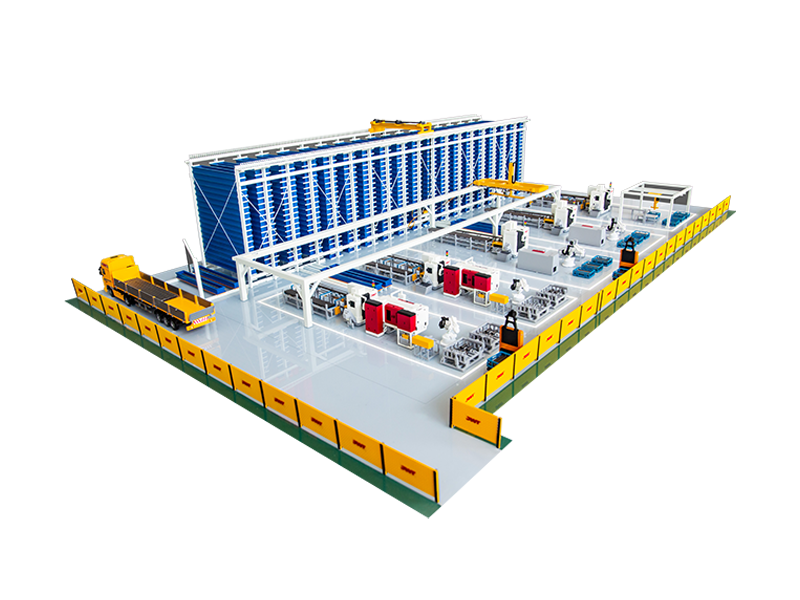
Beyond just cutting, advanced automated sawing equipment integrates sophisticated material handling capabilities that streamline the entire process:
-
Automated Feeding Systems: Many machines feature automatic loaders that feed raw material into the cutting zone, eliminating the need for manual positioning and significantly increasing throughput. This can include roller conveyors, push-feed systems, or robotic arms.
-
Nesting Software: For flat materials like sheets of wood, metal, or plastic, integrated nesting software is a game-changer. This function intelligently arranges multiple part shapes on a single sheet to maximize material utilization and minimize scrap. This not only saves on material costs but also reduces waste disposal.
-
Sorting and Stacking: After cutting, some advanced automatic saw machines can automatically sort cut pieces according to pre-programmed criteria and stack them, preparing them for the next stage of production or shipment.

Enhanced Safety Features
Automating the cutting process significantly enhances workplace safety. With an industrial cutting machine taking over the hazardous task of interacting directly with saw blades, the risk of operator injury is drastically reduced. Key safety functions include:
-
Enclosed Cutting Areas: Most automatic saws feature fully enclosed cutting zones, preventing operators from coming into contact with moving blades during operation.
-
Interlocks and Sensors: Safety interlocks ensure that the machine cannot operate if guards are open or if safety protocols are not met. Sensors detect the presence of material and operator proximity, stopping the machine if a hazardous situation is detected.
-
Automatic Blade Retraction and Braking: Blades automatically retract after a cut, and braking systems ensure rapid blade stop in case of an emergency or power interruption.
Data Integration and Programmability
Modern automated cutting machines are not just mechanical devices; they are intelligent systems capable of extensive data integration and sophisticated programmability.
-
CNC Control (Computer Numerical Control): This is perhaps the most defining function. Operators can program complex cutting patterns, sequences, and dimensions directly into the machine's control unit, allowing for highly precise and repeatable operations without manual intervention for each cut.
-
CAD/CAM Integration: Many automatic saw machines can directly import cutting programs from CAD (Computer-Aided Design) files and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software. This seamless integration speeds up the design-to-production workflow and reduces the chance of human error.
-
Production Monitoring and Reporting: Advanced models can collect data on production rates, material consumption, and machine performance. This data is invaluable for optimizing operations, scheduling maintenance, and tracking overall efficiency.
-
Remote Diagnostics and Connectivity: Some machines offer remote diagnostic capabilities, allowing technicians to troubleshoot issues off-site, and can be integrated into broader factory automation systems (Industry 4.0).
In conclusion, the functions of an automatic saw machine extend far beyond a simple cut. From precise material processing and intelligent optimization to enhanced safety and data-driven capabilities, these power cutting tools are integral to achieving high efficiency, consistency, and profitability in a wide array of industrial applications. As technology continues to advance, we can expect these machines to become even more sophisticated, further transforming manufacturing processes worldwide.



 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский