The Unsung Workhorse: Delving into Heavy-Duty Saw Machines
In the world of manufacturing, construction, and specialized fabrication, precision and power go hand-in-hand. While many tools play crucial roles, the heavy-duty saw machine stands out as an unsung workhorse, capable of tackling the most demanding cutting tasks with efficiency and accuracy. These formidable machines are far removed from their handheld cousins, designed for continuous operation, high-volume production, and the processing of exceptionally robust materials.
What Defines a Heavy-Duty Saw Machine?
The "heavy-duty" designation isn't merely a marketing buzzword; it refers to a combination of design features and capabilities that set these machines apart. Key characteristics include:
Robust Construction: Built with durable, high-grade materials, heavy-duty saws are designed to withstand significant stress, vibration, and continuous use without compromising performance or safety. This often means thick steel frames, reinforced components, and heavy-duty bearings.
Powerful Motors: Equipped with high-horsepower motors, these machines generate immense cutting force, allowing them to slice through dense metals, thick timber, composites, and other challenging materials that would bog down or damage lighter saws.
Precision and Stability: Despite their power, heavy-duty saws are engineered for remarkable precision. Their inherent stability, often due to their substantial weight and rigid construction, minimizes vibration and ensures clean, accurate cuts, even under heavy loads.
Advanced Cutting Mechanisms: Depending on the application, heavy-duty saws utilize various cutting mechanisms, including:
Band Saws: Ideal for cutting intricate shapes, curves, and often used for general-purpose metal and wood cutting. Heavy-duty band saws feature large throat capacities and powerful motors for thick stock.
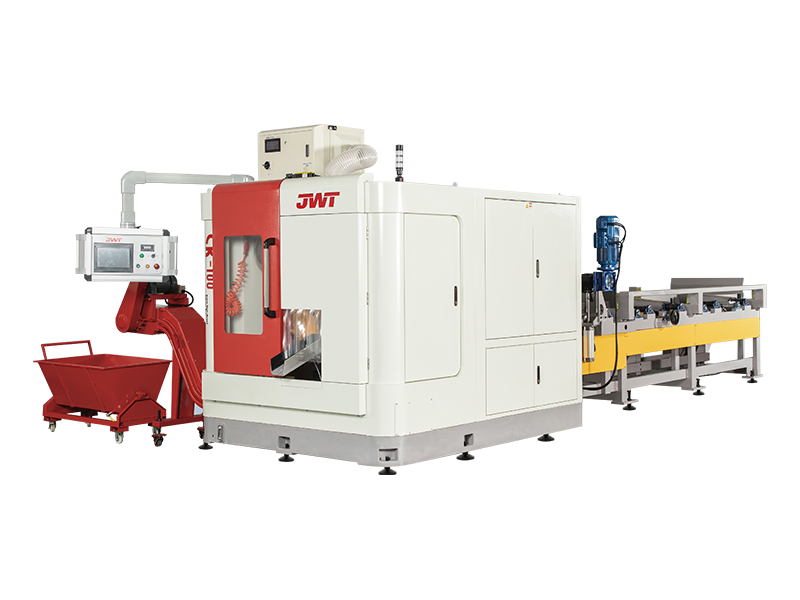
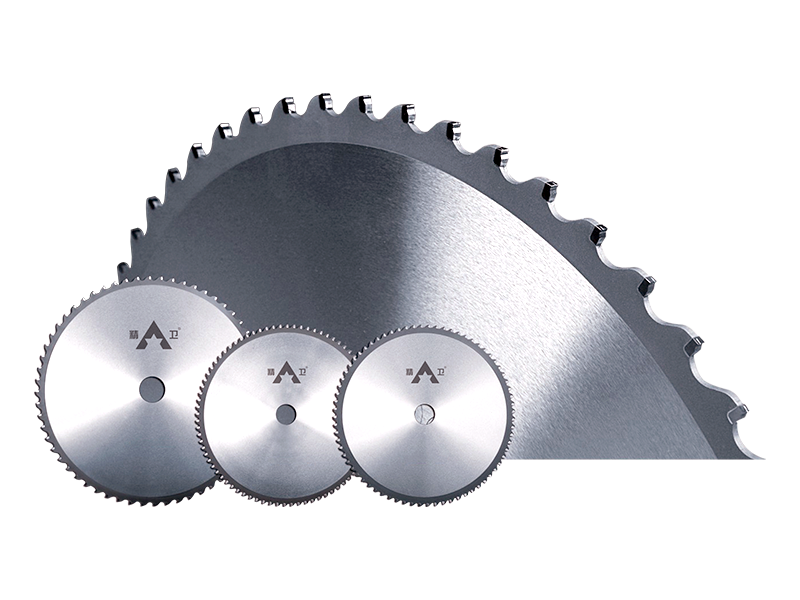
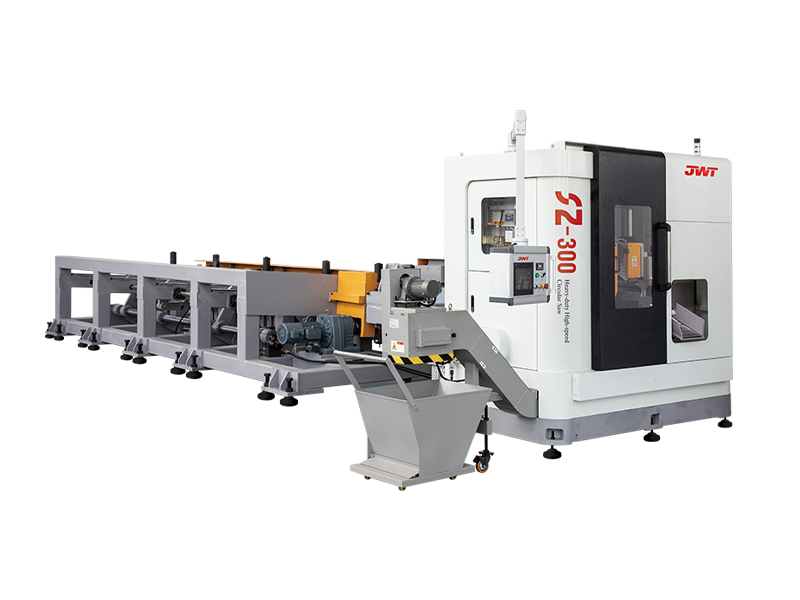
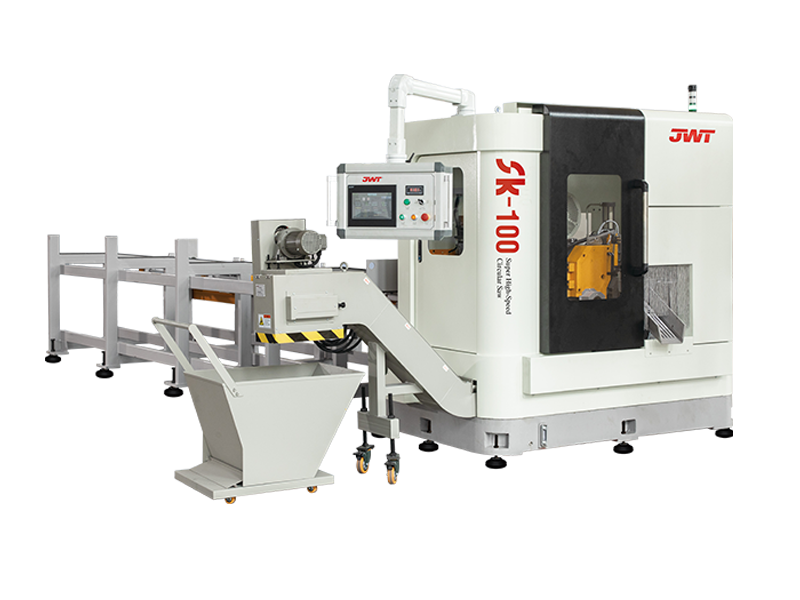
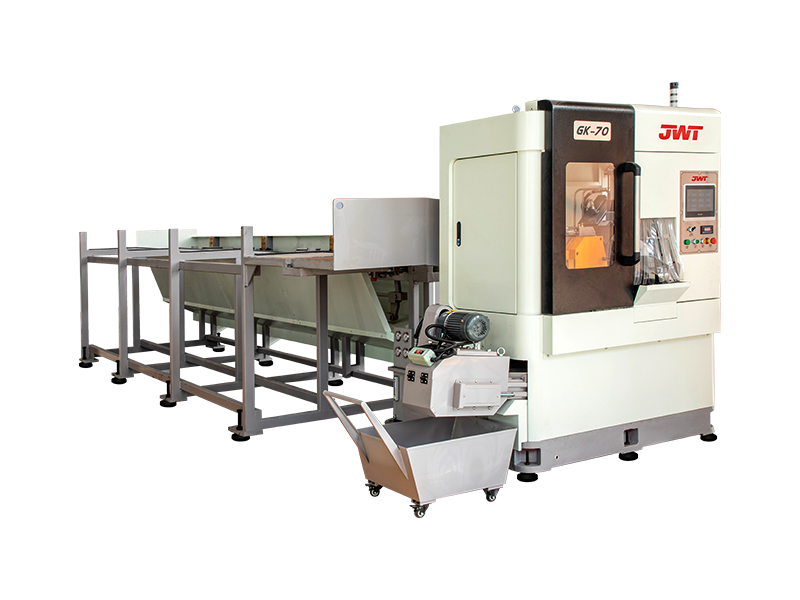
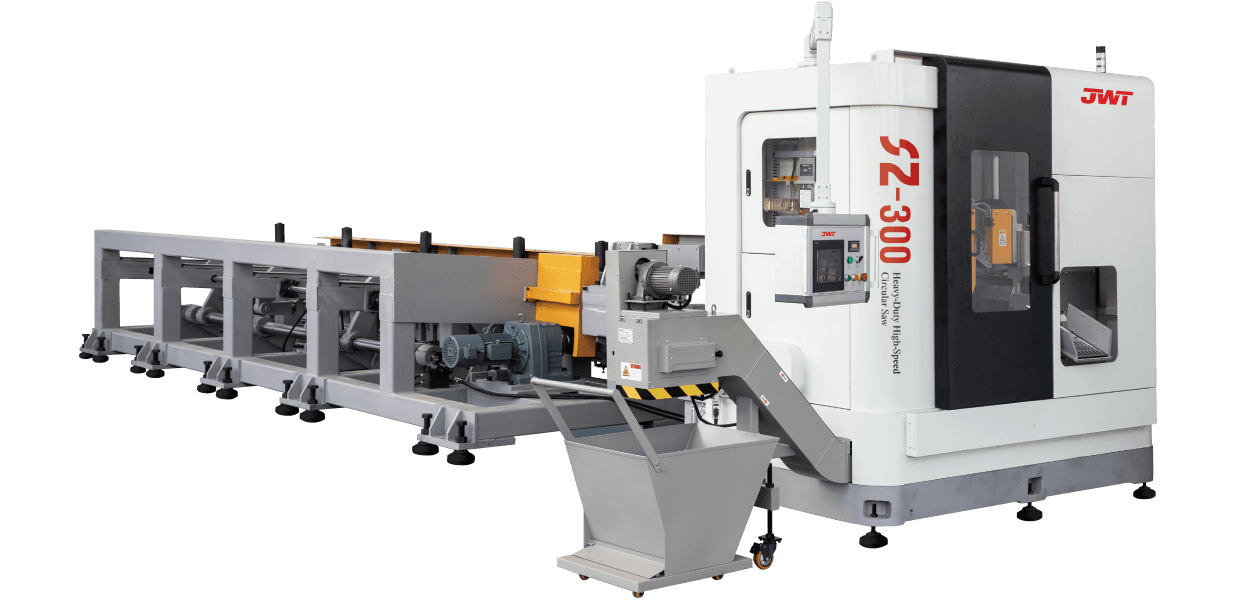
Circular Saws (Cold Saws/Abrasive Saws): Employing large, durable blades, these are common for cutting large sections of metal (cold saws for precise, burr-free cuts, abrasive saws for fast cuts on hardened materials).
Plate Saws: Specifically designed for cutting large sheets or plates of material, often found in metal fabrication and shipbuilding.
Beam Saws: Predominantly used in woodworking for precisely cutting large panels of wood, often with automated feeding and optimization software.
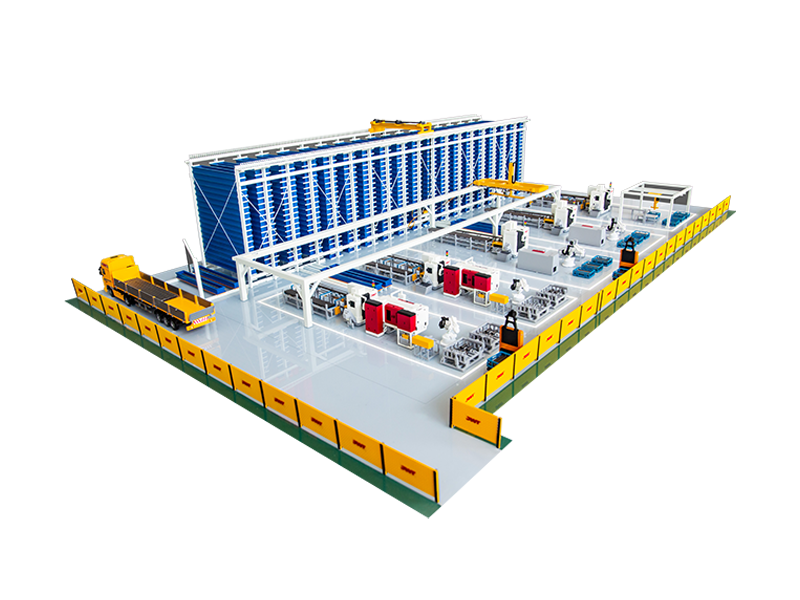
Automation and Safety Features: Many modern heavy-duty saws incorporate advanced automation for material feeding, clamping, and cutting, improving efficiency and reducing manual labor. Comprehensive safety features, such as blade guards, emergency stops, and interlocks, are paramount due to the inherent power of these machines.
Cooling Systems: For metal cutting, efficient cooling systems (often flood coolants) are essential to dissipate heat generated during the cutting process, extending blade life and preventing material distortion.
Applications Across Industries:
The versatility of heavy-duty saw machines makes them indispensable across a wide spectrum of industries:
Metal Fabrication: Cutting beams, pipes, plates, and various profiles for structural steel, machinery, and automotive components.
Construction: Processing large timber beams, steel rebar, and other construction materials on-site or in prefabrication yards.
Woodworking: Sizing large panels, processing rough lumber, and creating components for furniture, cabinetry, and architectural elements.
Aerospace: Cutting specialized alloys and composites with high precision for aircraft components.
Shipbuilding: Fabricating large metal sections for ship hulls and superstructures.
Foundries and Forging Plants: Trimming excess material from castings and forgings.
Recycling: Cutting down large, bulky materials for easier processing.
The Future of Heavy-Duty Sawing:
As industries continue to demand greater efficiency, precision, and automation, heavy-duty saw machines are evolving. We can expect to see:
Increased Integration with Robotics: For fully automated loading, unloading, and cutting processes.
Smarter Controls and IoT Connectivity: Allowing for remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized cutting parameters.
Enhanced Material Versatility: New blade technologies and cutting methods for increasingly complex and advanced materials.
Greater Energy Efficiency: More efficient motors and optimized cutting strategies to reduce power consumption.
In conclusion, the heavy-duty saw machine, though often operating behind the scenes, is a cornerstone of modern industrial production. Its ability to combine immense power with remarkable precision makes it an invaluable asset, enabling the creation of everything from skyscrapers and ships to intricate machinery, silently powering progress in countless sectors worldwide.



 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский