The Cutting Edge: Exploring the World of High-Speed Circular Saws
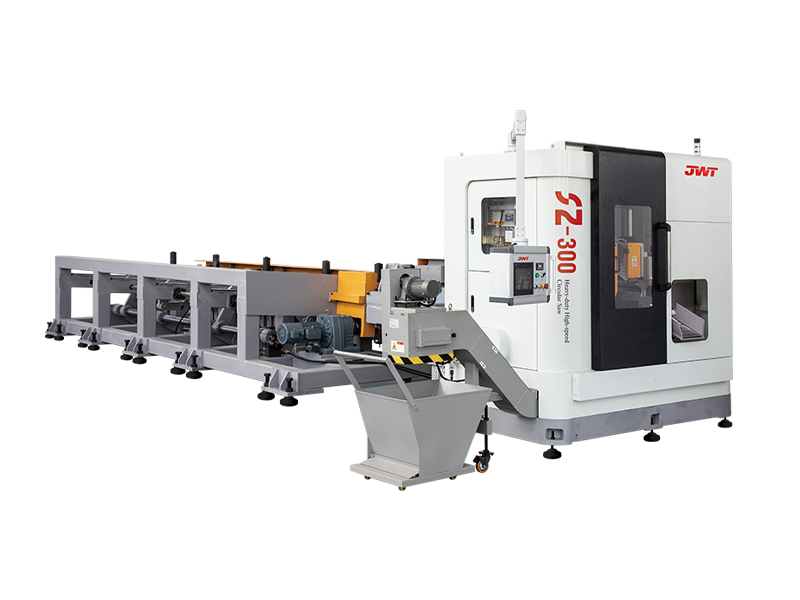
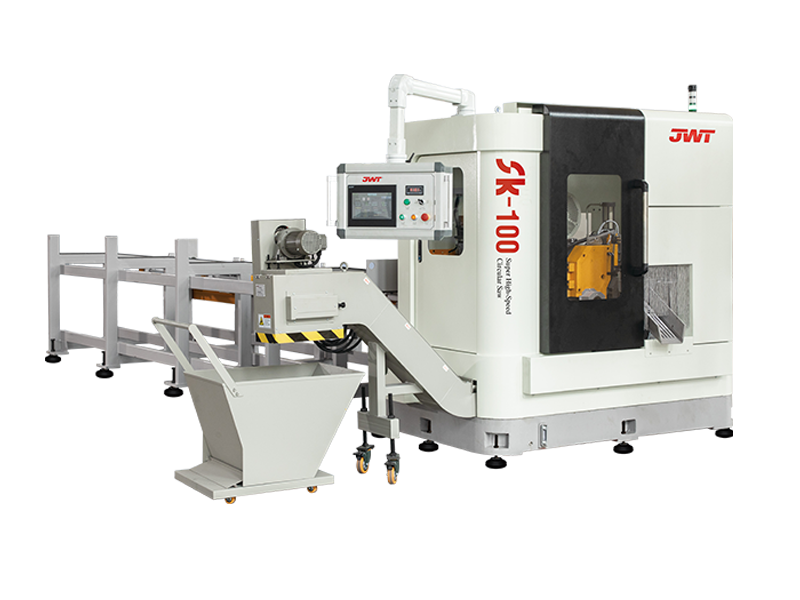
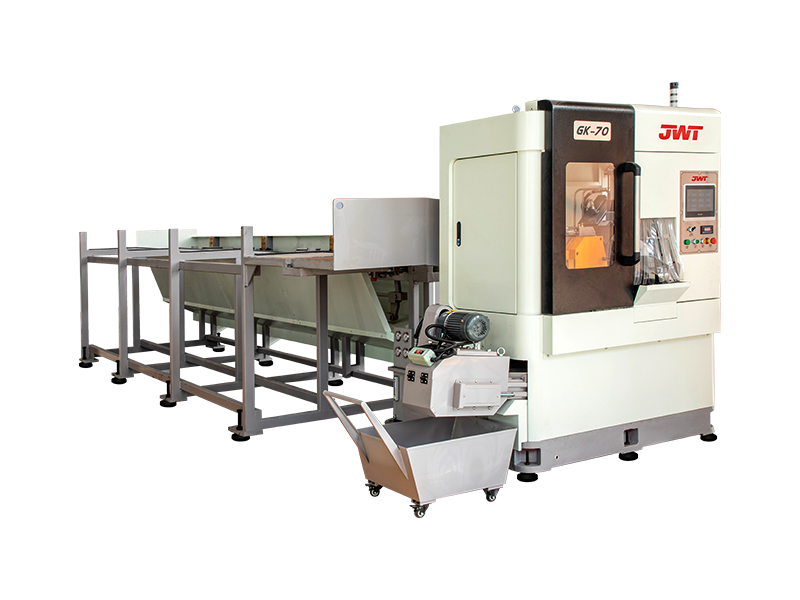
Circular saws are a staple in workshops and on job sites, but a new class of cutting tools is taking performance to the next level: super high-speed circular saws. These advanced machines are not just faster; they represent a significant leap in cutting technology, offering enhanced precision, efficiency, and material compatibility.
Understanding the Power Behind the Speed
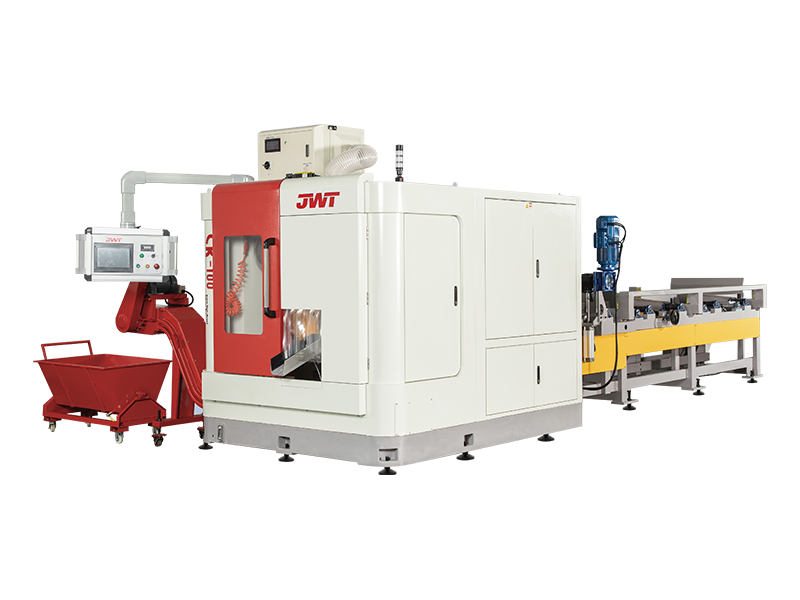
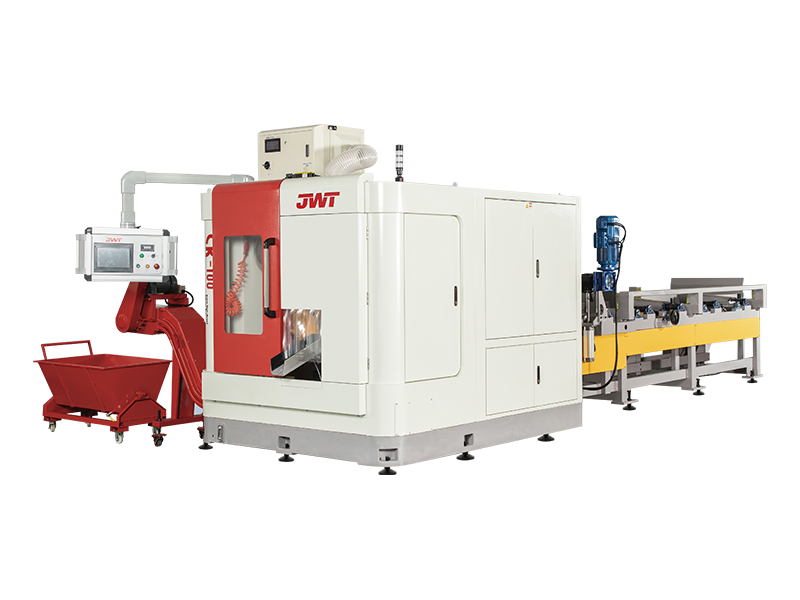
At its core, a circular saw uses a toothed blade that rotates at high speed to cut through materials. What distinguishes a super high-speed circular saw is its significantly higher RPM (revolutions per minute) rating. While a standard circular saw might operate at around 4,000 to 5,000 RPM, a high-speed model can easily exceed this, with some professional-grade units reaching 10,000 RPM or more.
This increased rotational speed translates directly into several key advantages:
- Cleaner Cuts: The faster a blade spins, the more precisely its teeth can interact with the material. This minimizes tearing and splintering, especially in delicate materials like laminates and fine woods. The result is a smooth, professional-grade finish that often requires little to no sanding or post-processing.
- Faster Workflows: Higher speeds mean materials are cut in a fraction of the time. This is particularly valuable in industrial settings or on large-scale construction projects where speed is critical for productivity.
- Reduced Wear and Tear: Counterintuitively, the faster speed can reduce the strain on both the saw and the blade. The blade’s teeth spend less time in contact with the material, which reduces heat buildup and friction. This can extend the life of the saw blade and the tool itself.
Key Features and Innovations
Beyond just speed, a super high-speed circular saw often incorporates several advanced features to manage its power and ensure user safety:
- Advanced Motor Technology: These saws are typically equipped with high-performance, brushless motors. Unlike traditional brushed motors, brushless designs are more efficient, generate less heat, and offer a better power-to-weight ratio. They are also more durable and require less maintenance.
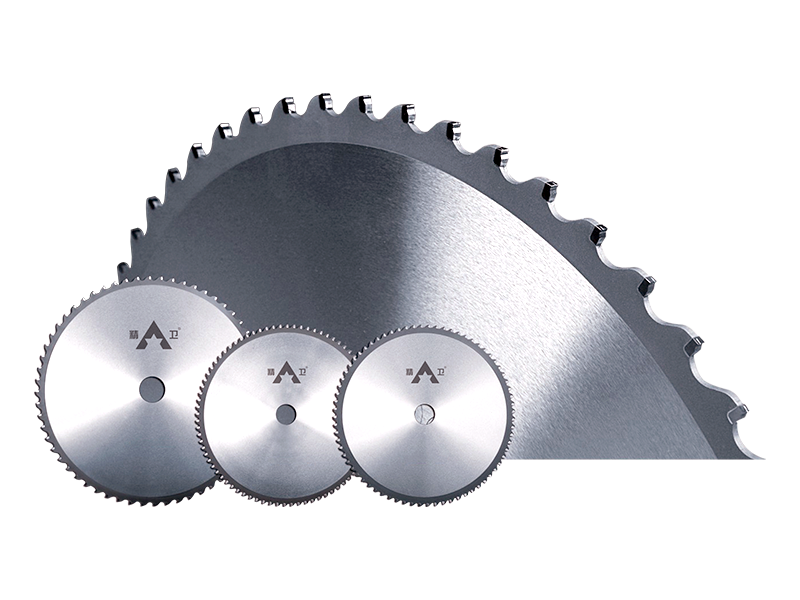
- Blade and Material Specificity: The high RPMs necessitate the use of specialized blades. Carbide-tipped blades with a high tooth count are common for clean cuts in wood and composite materials. For cutting metal, specific friction-cutting or cold-cut blades are used, designed to handle the intense heat generated at such high speeds.
- Enhanced Safety Features: The immense power and speed of these tools demand robust safety measures. Features like electronic brakes, which stop the blade almost instantly upon release of the trigger, and advanced blade guards are standard.
- Dust Management: The high-speed cutting action generates a significant amount of dust. Many high-speed models include integrated dust ports that can be connected to a vacuum system, keeping the workspace clean and improving visibility.
Applications and Future Outlook
The applications for a super high-speed circular saw extend beyond traditional woodworking. They are increasingly used in:
- Plastics and Composites: Their ability to make clean, precise cuts with minimal heat buildup makes them ideal for cutting acrylic, polycarbonate, and carbon fiber.
- Metal Fabrication: With the right blade, these saws can quickly and efficiently cut through aluminum, steel, and other metals, often replacing traditional abrasive cutters.
- Aerospace and Automotive Manufacturing: Precision and speed are paramount in these industries, making high-speed saws valuable tools for cutting specialized materials.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see super high-speed circular saws become more compact, efficient, and accessible. The future of cutting is not just about raw power, but about intelligent design that harnesses speed for superior results.



 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский